Total Hip Replacement
The Total Hip Replacement (THR) is a surgical procedure to replace a patient's diseased hip joint with a prosthetic implant. This procedure is performed for patients suffering from arthritis, fractures, or other conditions that affect the hip joint.
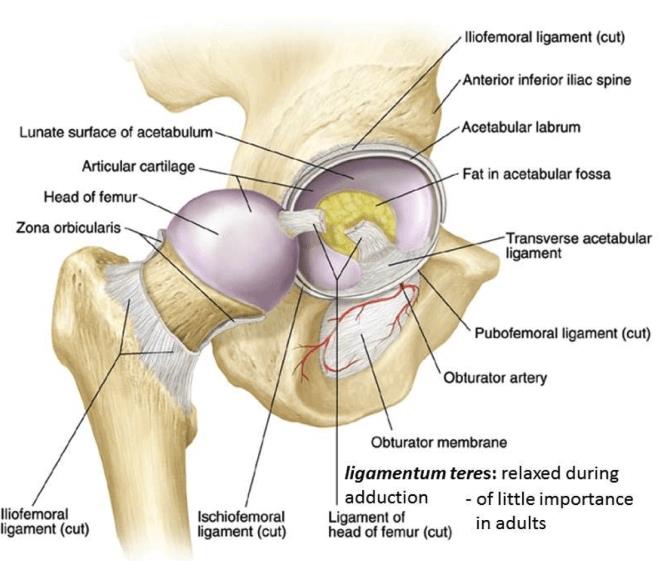
Relevant Anatomy
The THR procedure involves the acetabulum (hip socket) and femoral head (the ball of the thigh bone). An understanding of the anatomy surrounding the hip joint is critical for ensuring proper implant placement and minimizing complications.
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Basic Orthopaedic Tray (Sterile)
- Scalpel blades (No. 10, 15)
- Bone saw (oscillating or reciprocating)
- Bone chisels and osteotomes
- Metzenbaum scissors
- Needle holders (Mayo-Hegar)
- Bone rasp and reamers
- Forceps (DeBakey, Adson)
- Hemostatic clamps (Kocher, Hemoclip)
- Retractors (Weitlaner, Richardson)
- Suction tips (Yankauer and Frazier)
- Orthopaedic drill (for reaming femoral canal)
- Prosthetic components (Zimmer implants)
- Sutures (Prolene, Vicryl)
- Electrocautery (bovie with pencil and grounding pad)
Specialised Instruments
- Acetabular reamers and trial components
- Femoral reamers and trial components
- Positioning guides for alignment
- Femoral head extractor
Sutures
- 4-0, 5-0 Prolene (CV needles)
- 2-0 Vicryl (for deep tissue closure)
- Sternal closure wires (if needed for any thoraco-abdominal approach)
Other Equipment
- Hip prosthesis components (Zimmer total hip implants)
- Bone cement (if using cemented prostheses)
- Intravenous infusion pumps
- Haemostatic agents (Surgicel, Gelfoam)
- Defibrillator and paddles
- Cell saver (autotransfusion system)
- Pacing wires (if necessary for arrhythmias)
- Orthopaedic positioning support pads
Fluids and Medications
- Heparin: For anticoagulation prior to surgery (if needed)
- Saline solution: For irrigation and flushing
- Antibiotics: Prophylactic antibiotics as per protocol
- Fentanyl/Midazolam: For anesthesia and pain management
- Local anaesthetic: For peri-operative pain control
- Blood products: RBCs, platelets, and FFP available on standby
2. Before knife to skin
- Check and prepare all instruments
- Count and document all sponges, instruments, and needles
- Assist with prepping and draping (see next section)
- Ensure prosthesis is available and sterilized
- Prepare anaesthesia drugs and confirm with anaesthetist
Prepping and Draping
- Prep the hip, thigh, and groin area using appropriate antiseptic (alcoholic chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine)
- Use sterile towels to cover the unaffected side and genitalia
- Ensure sterile drapes are placed correctly over the surgical site and across the abdomen if necessary
- Apply a sterile field over the operating table
- Ensure the leg is positioned and draped for optimal access to the hip joint
- Ensure correct positioning for hip replacement, with the limb in slight traction and external rotation if required
3. Intraoperative Stages (Detailed)
- Skin Incision: Make a posterolateral or anterior approach incision depending on surgeon preference.
- Joint Exposure: Dissect through soft tissues to expose the hip joint capsule.
- Capsulotomy: Open the joint capsule and dislocate the femoral head.
- Femoral Head Extraction: Remove the femoral head and prepare the femoral canal using reamers.
- Acetabular Preparation: Ream the acetabulum and place trial components to assess fit.
- Implantation of Acetabular Component: Secure the acetabular cup into the prepared acetabulum using screws or cement (if applicable).
- Femoral Component Insertion: Prepare and insert the femoral stem and head, ensuring proper alignment and fit.
- Trial Reduction: Perform a trial reduction to assess joint stability and range of motion.
- Final Implantation: Secure the final prosthesis components in place.
- Wound Closure: Close the joint capsule, fascia, and skin with sutures or staples.
- Post-operative Hemostasis: Ensure adequate haemostasis before closure.
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final instrument and sponge count
- Assist with sterile drape removal and patient transfer
- Dispose of contaminated disposables and prepare instruments for sterilization
- Complete surgical documentation and handover to recovery
- Ensure the hip joint is functioning properly in recovery before transferring to post-op care or ICU