Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction via Knee Arthroscopy
A knee arthroscopy with ACL reconstruction is a minimally invasive orthopaedic procedure to replace a torn anterior cruciate ligament using a graft (e.g., hamstring, patella tendon, or allograft) under arthroscopic guidance.
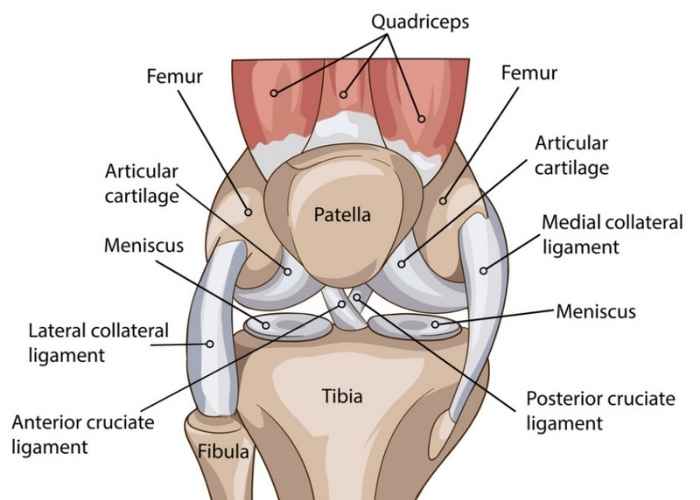
Relevant Anatomy
The knee joint includes the femur, tibia, patella, menisci, cruciate and collateral ligaments. The ACL runs diagonally through the knee, providing rotational stability.
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Arthroscopy Tray (Sterile)
- Scalpel blades (No. 11, 15)
- Mayo and Metzenbaum scissors
- Tissue forceps (toothed, Adson, DeBakey)
- Needle holders
- Arthroscopic camera, light cable, and monitor setup
- Arthroscopy pump and tubing
- Trocar and sheath sets (anterolateral, anteromedial portals)
- Probes, shaver, burrs, and curettes
- Suction (Frazier/Yankauer)
ACL Instrument Set
- Drill guides and aiming device (for femoral and tibial tunnels)
- Reamers (4.5 mm–10 mm, depending on graft size)
- Graft preparation board and tensioner
- Suture passer, loopers, and grasper
- Interference screws or suspensory fixation devices (e.g., EndoButton)
Sutures
- Orthocord or high tensile strength sutures for graft fixation
- 3-0 Vicryl or Monocryl for subcutaneous tissue
- 3-0 or 4-0 Nylon for skin closure
Other Equipment
- Tourniquet and control unit
- Leg holder for flexion and stabilisation
- Arthroscopic tower (camera, pump, light, shaver)
- Pulse lavage for irrigation (optional)
- Sterile dressing supplies and compression bandage
- Knee drapes or extremity drape pack
Fluids and Medications
- Antibiotics: Cefazolin IV pre-op (per hospital protocol)
- Normal saline or glycine: For arthroscopy irrigation
- Local anaesthetic: Ropivacaine or bupivacaine with/without adrenaline (surgeon preference)
- Tranexamic acid (TXA): May be used intra-articularly or systemically
2. Before Knife to Skin
- Ensure all camera, shaver, and pump systems are functioning and primed
- Complete initial count of instruments, swabs, and sharps
- Set up graft prep station (if using hamstring graft)
- Check and open all fixation devices as per surgeon request
- Coordinate with radiographer if intraoperative imaging is planned
Prepping and Draping
- Prep entire leg from mid-thigh to foot using alcoholic chlorhexidine
- Apply tourniquet (do not inflate until directed)
- Secure leg in leg holder with foot hanging freely
- Drape using knee arthroscopy drape or full extremity drape set
3. Intraoperative Stages
- Diagnostic Arthroscopy: Insert camera, inspect joint, lavage, address meniscal pathology if present
- Graft Harvesting (if autograft): Harvest hamstring or patella tendon; prep on graft board
- Tunnel Preparation: Use drill guides to create femoral and tibial tunnels
- Graft Insertion: Pass graft via shuttle suture; tension appropriately
- Fixation: Secure graft with screws or buttons as per technique
- Final Inspection: Confirm graft placement and range of motion arthroscopically
- Irrigation and Closure: Lavage joint, close portal incisions, apply dressing
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final count of instruments, sharps, and swabs
- Apply sterile dressings and compression bandage
- Document implants used (type, size, batch number)
- Assist with transfer and leg positioning for PACU
- Clean, soak, and repack instruments as per CSSD protocol
- Handover to recovery nurse including procedure summary and fixation details