External Ventricular Drain (EVD) Insertion
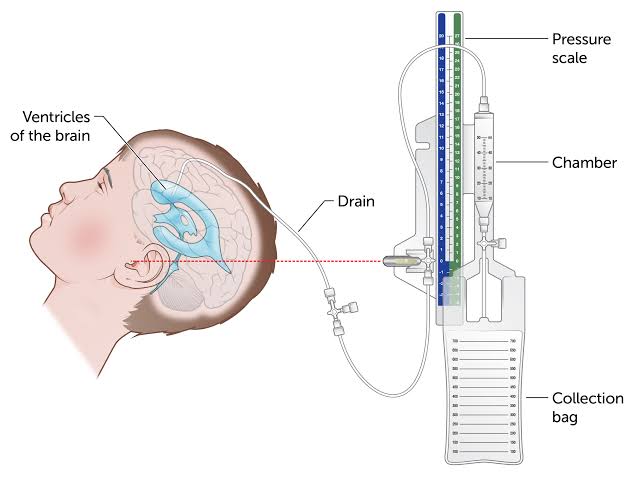
An External Ventricular Drain (EVD) is a neurosurgical procedure used to relieve elevated intracranial pressure by draining cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the ventricles of the brain. It is a sterile, high-risk procedure typically performed in emergency or ICU settings.
Relevant Anatomy
The EVD catheter is usually inserted through a burr hole at Kocher’s point, passing into the lateral ventricle. Accurate anatomical knowledge of the frontal lobe, midline, and foramen of Monro is critical. Visit this site for more information on External ventricular drain
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Neurosurgical Minor Tray (Sterile)
- Scalpel blades (No. 10, 11, 15)
- Mayo and Metzenbaum scissors
- Adson forceps (toothed and non-toothed)
- Needle holders
- Perforator or Hudson brace with burr
- Dura hooks or elevators
- Suction tips (Yankauer, Frazier)
- Bipolar diathermy forceps and cable
Specialised Equipment
- EVD catheter and drainage system (e.g. Codman or Bactiseal)
- Connecting tubing and burette
- CSF drainage bag and pole
- Sterile ruler and marker
- Drill with burr attachments (if not using manual perforator)
Sutures
- 3-0 or 4-0 Nylon for securing catheter
- 3-0 Vicryl or Monocryl for skin closure
Other Equipment
- Sterile towels and head drapes
- Antimicrobial drape (e.g. Ioban)
- Transparent occlusive dressing (e.g. Tegaderm)
- Chlorhexidine/alcohol prep solution
- Sterile gloves and gown for assistant
Fluids and Medications
- Antibiotics: Cefazolin or per neurosurgeon’s orders, given IV pre-op
- Local anaesthetic: Lignocaine 1% with or without adrenaline
- Normal saline: For irrigation or flushing
- Bone wax: May be used for haemostasis at burr hole site
2. Before Knife to Skin
- Perform initial count of instruments, sharps, and swabs
- Prepare and layout sterile instruments on scrub trolley
- Confirm EVD catheter system is available, sterile, and compatible
- Assist team with patient positioning (typically supine with head neutral)
- Ensure drill or manual perforator is functioning and sterile
Prepping and Draping
- Prep scalp with alcoholic chlorhexidine solution
- Use head drape or neurosurgical field drapes
- Ensure CVC/lines are clear of operative site
- Drape to maintain full sterility and visual access to head
3. Intraoperative Stages
- Incision and Burr Hole: Make linear incision at Kocher's point and create burr hole using perforator
- Dura Opening: Carefully nick dura using needle tip or hook
- Catheter Insertion: Advance EVD catheter toward foramen of Monro (approx. 5–6 cm depth)
- Confirmation: Observe CSF flow; connect to closed drainage system
- Securing Catheter: Suture catheter to scalp and apply dressing
- Closure: Close incision site as per protocol
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final count of instruments, sharps, and swabs
- Ensure EVD is labelled, secured, and clamped or unclamped per order
- Record length of catheter inserted and drainage level
- Clean instruments and dispose of sharps per hospital policy
- Complete documentation and implant log (if applicable)
- Hand over to ICU or PACU staff with drain details