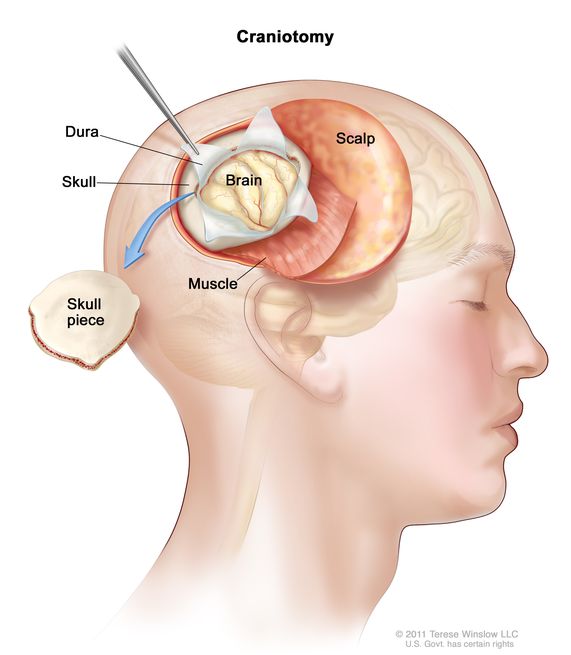
Craniotomy Procedure
A Craniotomy is a neurosurgical procedure where a bone flap is temporarily removed from the skull to access the brain. It may be performed for tumour removal, aneurysm clipping, hematoma evacuation, or trauma management.
Relevant Anatomy
The cranium encloses the brain and includes the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital bones. Key structures include the dura mater, cerebral lobes, venous sinuses, and surrounding vasculature.
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Basic Neurosurgical Tray (Sterile)
- Scalpel blades (No. 10, 11, 15)
- Mayo scissors (curved and straight)
- Metzenbaum scissors
- Tissue forceps (Adson, DeBakey, bayonet)
- Needle holders (standard and micro)
- Periosteal elevator (Penfield, Freer)
- Self-retaining retractors (Weitlaner, Leyla, Greenberg frame)
- Electrocautery (bovie pencil with neurosurgical tip)
- Bone flap craniotome system (e.g. Midas Rex or Anspach drill)
- Craniotome footplate and attachments
- Suction (Yankauer and Frazier tips)
Specialised Instruments
- Dura hooks and scissors
- Dural tenting sutures and forceps
- Aneurysm clips and appliers (if relevant)
- Neurosurgical microscope (if required)
- Ultrasonic aspirator (e.g. CUSA)
Sutures
- 4-0 or 5-0 Nurolon or Silk (dural closure)
- 3-0 or 4-0 Monocryl/Vicryl (subcutaneous closure)
- 2-0 or skin staples (skin closure)
Other Equipment
- Headrest (Mayfield 3-pin clamp and horseshoe options)
- Patient positioning gel pads
- Neuro patties (cottonoids)
- Bone wax
- Drain (e.g. Jackson-Pratt or subgaleal)
- Sterile dressings and head bandage wrap
Fluids and Medications
- Antibiotics: Cefazolin IV per hospital protocol
- Normal saline: Irrigation (including with syringe or bulb)
- Local anaesthetic: Bupivacaine or lignocaine with adrenaline (for scalp block)
- Mannitol: May be administered IV to reduce intracranial pressure
- TXA: Possibly used to reduce intra-op bleeding
2. Before Knife to Skin
- Ensure Mayfield head clamp and table setup is correct and secured
- Lay out and check all trays and specialist neurosurgical equipment
- Initial count of all instruments, swabs, patties, and sharps
- Confirm all implants/clips are available and sterile
- Coordinate with anaesthetic team for patient positioning and brain relaxation meds
Prepping and Draping
- Prep scalp with alcoholic chlorhexidine, including behind ears if needed
- Drape with neurosurgical head drape system or extremity pack with Ioban
- Ensure bovie and suction cables are secure and sterile
- Protect eyes and ensure face is accessible if required by anaesthetics
3. Intraoperative Stages
- Scalp Incision: Typically a question mark or linear incision depending on location
- Haemostasis: Achieved using bovie, clips, and haemostatic agents
- Craniotomy: Burr holes drilled and bone flap removed with craniotome
- Dura Opening: Dural flap incised and retracted to expose brain
- Procedure Specific Task: Tumour resection, hematoma evacuation, aneurysm clipping, etc.
- Dura Closure: Sutured watertight or with dural substitute
- Bone Flap Refixation: Secured with mini plates and screws or left off in decompressive cases
- Scalp Closure: Layered closure with drain inserted as required
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final count of instruments, swabs, patties, and sharps
- Apply sterile head dressing
- Ensure patient positioning aids are removed and skin checked
- Assist with safe transfer to PACU with head supported
- Complete intra-op documentation including implants, clips, and drain details
- Handover to PACU nurse and include any intraoperative events