Procedure Overview
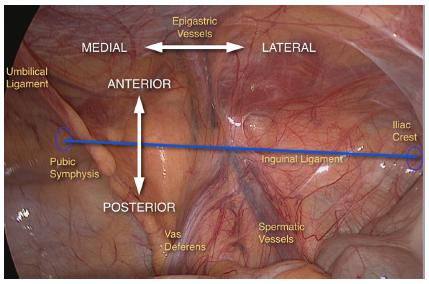
This is a laparoscopic total extraperitoneal (TEP) repair of a right inguinal hernia using Parietene mesh and AbsorbaTack fixation. Key anatomical structures include the inguinal canal, inferior epigastric vessels, peritoneum, and cord structures.
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Laparoscopic Tray (Sterile)
- Veress needle
- Trocar set (3 ports: 1x 10mm, 2x 5mm)
- 30° laparoscope
- Laparoscopic grasper (atraumatic)
- Laparoscopic scissors
- Laparoscopic diathermy hook
- Suction/irrigation set
- Needle holder (laparoscopic)
- AbsorbaTack device
Other
- Parietene mesh (approx. 10x15 cm)
- Electrocautery unit
- CO2 insufflator and tubing
- Light source and camera tower
- Saline for irrigation
Scrub Nurse Station
- Stand on the patient's left side (opposite the hernia site)
- Maintain sterile field and instrument handover
- Coordinate with the circulating nurse for device prep (e.g., AbsorbaTack)
2. Patient Setup
- Position: Supine, arms tucked or extended
- Bladder catheterisation: Optional but often used
- Skin prep: Umbilicus to mid-thigh, laterally to both flanks
- Draping: Standard laparotomy drape with adhesive window
3. Surgical Steps
- Incision and access: Infraumbilical incision for Veress needle or open Hasson technique. Establish CO2 pneumoperitoneum (10-12mmHg).
- Trocar insertion: Insert 10mm camera port infraumbilically. Under vision, insert two 5mm working ports in the lower abdomen (midline or paramedian).
- Dissection: Develop the preperitoneal space bluntly with camera and balloon dissector if needed.
- Identification: Identify anatomical landmarks – inferior epigastric vessels, pubic tubercle, Cooper’s ligament, vas deferens, and testicular vessels.
- Hernia sac management: Reduce the hernia sac. Blunt or sharp dissection is used, ensuring peritoneum remains intact.
- Mesh placement: Insert Parietene mesh, ensuring full coverage of the myopectineal orifice (including indirect, direct, and femoral spaces).
- Mesh fixation: Use AbsorbaTack to secure mesh to Cooper’s ligament, lateral abdominal wall, avoiding nerve injury zones.
- Desufflation and closure: Release CO2, remove trocars, close fascia at 10mm port, and skin closure with Monocryl or skin glue.
4. Postoperative Considerations
- Instrument count verification
- Ensure mesh and fixation device packaging is accounted for and documented
- Assist with patient transfer to recovery
- Clean and pack laparoscopic instruments for reprocessing