Ross Procedure
The Ross procedure is a complex open-heart surgery where the patient's diseased aortic valve is replaced with their own pulmonary valve (autograft), and the pulmonary valve is then replaced with a donor valve (homograft). As a scrub nurse in Australia, you must be thoroughly prepared with the correct instruments, equipment, positioning and a surgical step by step.
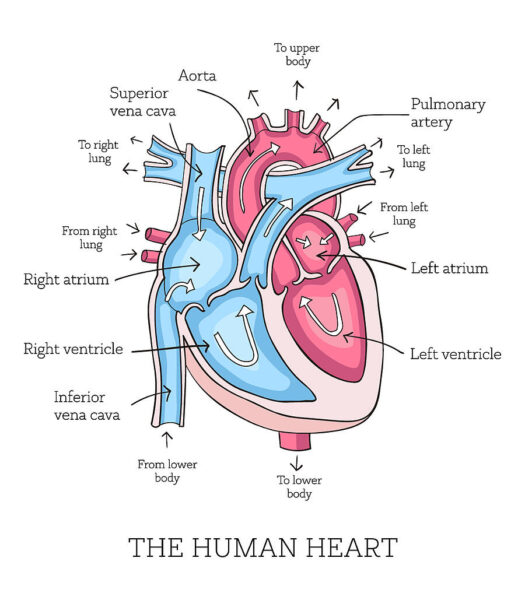
Relevant Anatomy
The Ross procedure involves structures of both the aortic and pulmonary valve. Awareness of spatial relationships is key during autograft harvesting and homograft implantation.
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Basic Cardiac Tray (Sterile)
- Scalpel blades (No. 10, 15, 11)
- Metzenbaum scissors (curved and straight)
- Mayo scissors (straight and curved)
- Vascular scissors (Potts, DeBakey)
- Needle holders (Mayo-Hegar, Castroviejo)
- Tissue forceps (DeBakey, toothed and non-toothed)
- Vascular forceps (Cooley, DeBakey)
- Retractors (Finochietto rib spreader, Weitlaner, Alm, Richardson)
- Suction tips (Yankauer and fine Frazier)
- Vascular clamps (Satinsky, Bulldog, DeBakey)
- Aortic cross-clamp
- Valve sizers (for homograft and autograft)
- Sternal wires and wire twister
- Electrocautery (bovie with pencil and grounding pad)
Specialised Instruments
- Coronary ostia buttons punch
- Annuloplasty ring sizers (optional)
- Valve leaflet measuring tools
- Vascular dilators
- Suture booties (umbilical tapes or silicone vessel loops)
- Vascular tunnelling instruments (optional)
Sutures
- 4-0, 5-0, 6-0 Prolene (CV needles)
- 2-0, 3-0 Ethibond
- 4-0 Monocryl or PDS
- Sternal closure wires (steel)
Valves and Tissues
- Autograft (patient's pulmonary valve)
- Homograft (cryopreserved pulmonary valve)
Other Equipment
- Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) machine
- Cardioplegia system and tubing
- Heater-cooler unit
- Cell saver (autotransfusion system)
- Defibrillator and paddles
- Sterile ice slush
- Sterile saline, heparinised saline
- Pacing wires and generator
- Haemostatic agents (Surgicel, Floseal, Gelfoam)
Fluids and Medications
- Heparin: For anticoagulation prior to cannulation
- Cardioplegia solution: Delivers myocardial protection during arrest
- Saline and heparinised saline: For irrigation and flushing lines
- Protamine: To reverse heparin post-CPB
- Adrenaline/Noradrenaline: For blood pressure support if needed
- Blood products: RBCs, FFP, platelets available on standby
2. Before knife to skin
- Check and prepare all instruments
- Count and document all sponges, instruments, and needles
- Assist with prepping and draping (see next section)
- Prepare CPB tubing and cannulation instruments
- Ensure homograft is thawed per protocol and available
Patient Positioning
- Position: Supine position on the operating table.
- Support: A gel pad or pressure-relieving mattress to protect pressure points.
- Arms: Tucked at the sides with padding, or extended on armboards depending on anaesthetist preference.
- Head: Positioned in neutral alignment with head ring or support pad.
- Straps: Safety straps placed across thighs and arms to prevent falls or movement.
- ECG & Lines: Ensure ECG leads, arterial lines, and central lines are secured and accessible.
- Sterile Field Prep: Chest, abdomen, and groin area prepped for potential femoral access.
Skin Prepping and Draping
- Prep entire chest, abdomen, and groin area (+/- legs and feet)
- Use alcoholic chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine scrub per protocol
- Allow adequate drying time before sterile draping
- Apply large cardiac drape with fenestration over the sternum (might involve multiple layers of draping, leg lifting manoeuvres, head bar for the anaesthetics team)
- Ensure CPB lines are routed and anchored without contamination
3. Intraoperative Stages
- Midline Sternotomy: Use sternal saw and bone wax. Insert rib spreader carefully.
- Pericardiotomy & Exposure: Open pericardium, suspend with stay sutures or slings.
- Systemic Heparinisation: Ensure ACT monitoring; pass heparin via anaesthetist.
- CPB Cannulation: Aortic and right atrial cannulation; assist with sutures, clamps, ties.
- Initiate CPB & Cool Patient: Monitor ice slush and cooling circuit.
- Aortic Cross-Clamp & Cardioplegia: Deliver antegrade or retrograde cardioplegia.
- Aortic Valve Excision: Remove native valve; pass scissors, forceps, valve sizers.
- Harvest Pulmonary Autograft: Carefully dissect and mobilize pulmonary valve.
- Implant Autograft in Aortic Position: Secure with 5-0/6-0 Prolene sutures.
- Implant Pulmonary Homograft: Place homograft in RVOT; check orientation and sizing.
- De-airing & Reperfusion: Assist with warm saline syringes; monitor heart rhythm.
- Weaning from CPB: Assist with cannula removal, protamine administration.
- Achieve Haemostasis: Use Surgicel, Floseal, clips, or cautery as needed.
- Chest Closure: Reapproximate sternum using steel wires; layer closure of tissue and skin.
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final instruments and accountable item count and check
- Assist with sterile drape removal and patient transfer
- Dispose of all contaminated disposables and organise instruments compactly for transfer to SPC (sterilisation centre)
- Complete documentation and ensure correct, complete, and signed.
- Send off specimens (if any) for pathology
- Handover to recovery or (if pt transferring ICU, handover at least 30 minutes before procedure finishes)