Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
A CABG is a cardiac surgical procedure that restores blood flow to the heart by grafting vessels (typically the saphenous vein, radial artery, or internal mammary artery) to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries.
Relevant Anatomy
The procedure involves the heart, coronary arteries, and potential graft vessels (internal mammary artery, saphenous vein, or radial artery). The sternum is typically divided via median sternotomy for access.
Visit this site for a more detailed analysis of the coronary arteries of the heart.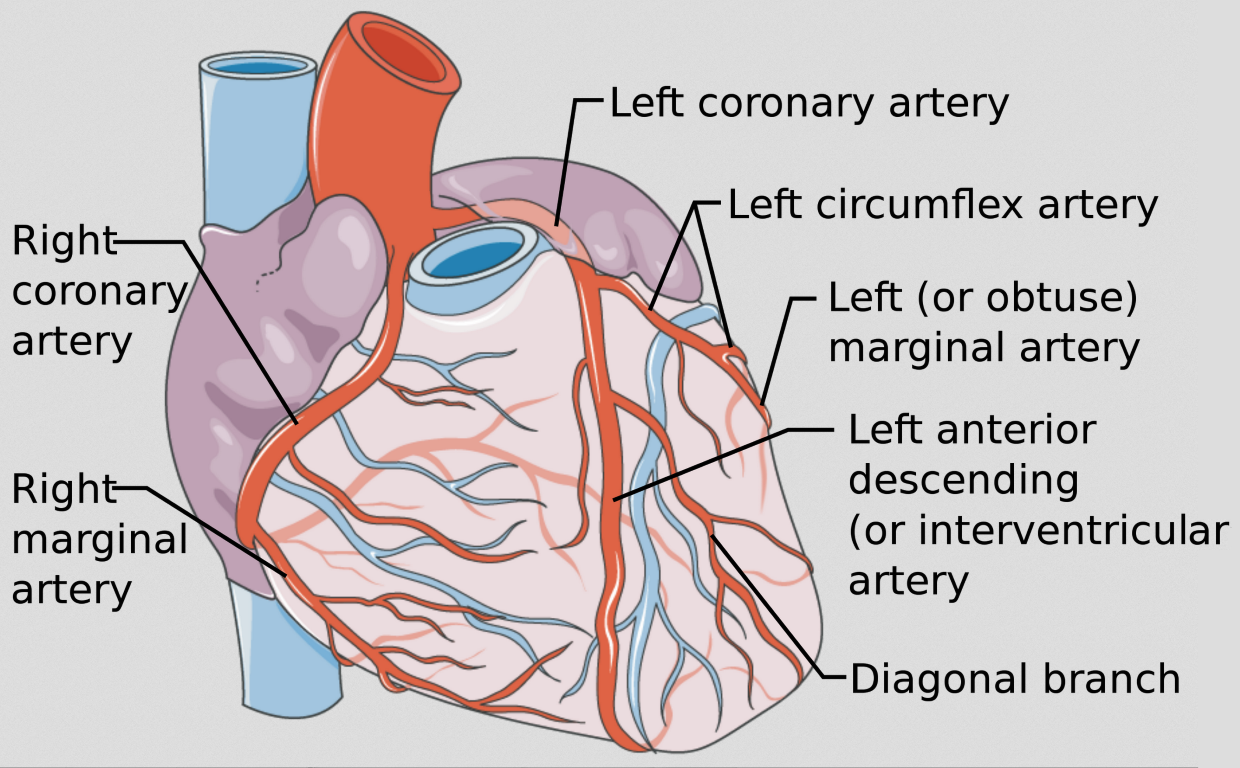
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
Cardiac Instrument Tray (Sterile)
- Sternal saw and sternal retractor (e.g. Finochietto)
- Vessel loops and bulldog clamps
- Potts scissors, DeBakey forceps
- Metzenbaum scissors, Mayo scissors
- Vascular clamps (Satinsky, Cooley)
- Needle holders (Castroviejo, Mayo-Hegar)
- Electrocautery (bovie)
- Suction (Yankauer and cardiotomy sucker)
- Coronary vessel dilators and stabilisers
Specialised Equipment
- Cardiopulmonary bypass machine (perfusionist managed)
- Cardioplegia setup
- Heater-cooler unit
- Cell saver system (if available)
- Ultrasound or flow probe (surgeon preference)
Sutures
- Prolene 6-0 to 8-0 for coronary anastomosis
- Vicryl or PDS for deep closure
- Sternal wires (stainless steel)
- Skin closure: staples or Monocryl 4-0
Other Equipment
- Sternal drapes / cardiac extremity pack
- Warming blanket / patient warming system
- Defibrillator and paddles
- Chest drains x 2 (Blake or Atrium)
- Suction tubing and collection system
- Sterile dressings and sternal support binder
Fluids and Medications
- Antibiotics: Cefazolin IV per protocol pre-op
- Heparin: Administered before bypass
- Protamine: Used to reverse heparin post-bypass
- Cardioplegia solution: Cold blood or crystalloid solution to arrest the heart
- Normal saline / Hartmann’s: For irrigation and fluid management
2. Before Knife to Skin
- Confirm availability of bypass machine and perfusion team
- Open and lay out all required cardiac trays and sutures
- Initial count of instruments, sharps, and swabs
- Ensure defibrillator is tested and ready
- Check blood products availability (as per anaesthetist)
Prepping and Draping
- Prep chest and both legs/arms (if harvesting vein or radial artery)
- Use alcoholic chlorhexidine solution (unless contraindicated)
- Drape using full cardiac pack and transparent adhesive drapes
- Maintain strict aseptic technique around sterile perfusion lines
3. Intraoperative Stages
- Sternotomy: Median sternotomy and sternal retraction
- Conduit Harvest: Harvest vein or artery (may be endoscopic or open)
- Heparinisation: Systemic heparin administered
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Cannulation and initiation
- Cardioplegia: Heart arrested using cardioplegia
- Anastomosis: Grafts sewn to coronary arteries using fine Prolene
- Wean off bypass: Monitor cardiac output and rhythm
- Protamine given: To reverse heparin effects
- Haemostasis and closure: Secure all grafts, place drains, close sternum with wires
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final count of swabs, sharps, and instruments
- Apply sterile dressing and chest binder
- Assist with patient transfer and secure drains and lines
- Ensure documentation of bypass time, grafts, and equipment used
- Hand over to ICU/PACU nurse with full details including grafts, drains, and post-op orders