Mastoidectomy
A mastoidectomy is an ENT surgical procedure involving the removal of infected mastoid air cells located in the mastoid bone behind the ear. It is often performed to treat chronic otitis media, mastoiditis, or cholesteatoma. Proper setup and understanding of anatomy, instruments, and workflow is essential for scrub nurses assisting in this procedure.
Relevant Anatomy
The mastoid bone is part of the temporal bone and contains air cells that communicate with the middle ear. The proximity to structures such as the facial nerve, sigmoid sinus, and semicircular canals makes surgical precision vital.
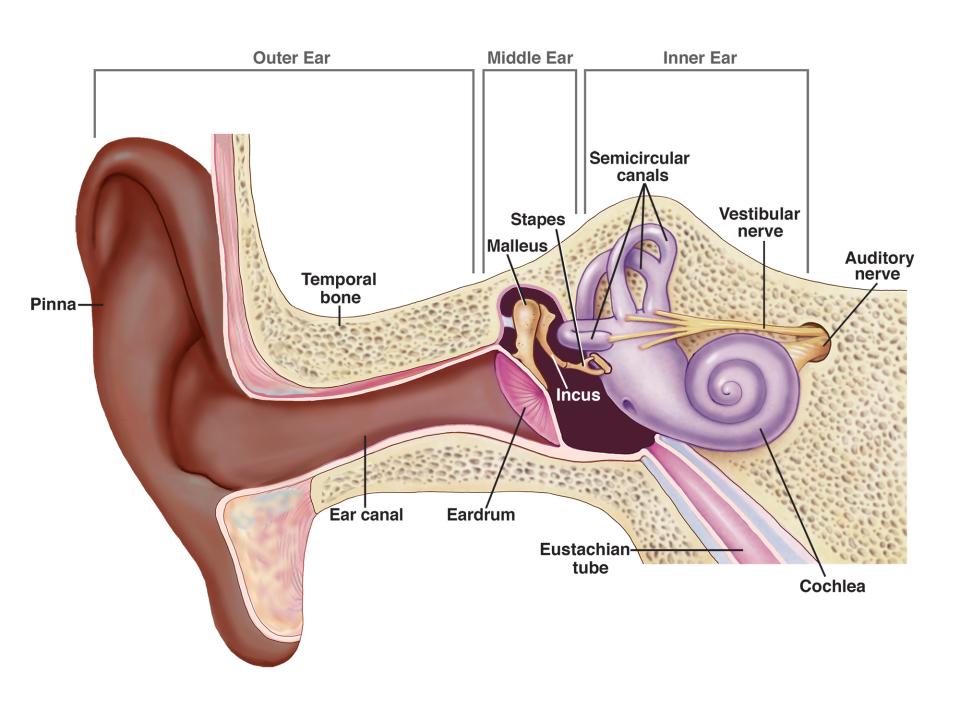
1. Instruments and Equipment Checklist
ENT Surgical Tray (Sterile)
- Scalpel blades (No. 15, 11)
- Fine dissecting scissors
- Ear speculum set
- Micro ear instruments (House, Rosen picks, suction dissectors)
- Self-retaining retractors (Weitlaner, McPherson)
- Fine suction tips (Frazier)
- Drill system with burrs (diamond and cutting)
- Microsurgical instruments (forceps, curettes, hooks)
Sutures
- 5-0, 6-0 Monocryl or Vicryl for skin and soft tissue closure
Other Equipment
- Operating microscope
- Ear prep pack (betadine, drapes, ear wicks)
- Head ring and support pad
- Diathermy unit with fine tip
- Suction and irrigation setup
- Fibrin sealant or haemostatic agents (optional)
2. Before Knife to Skin
- Confirm patient identity, consent, and surgical site marking
- Ensure microscope is functioning and focused
- Check ENT drill and burrs are available and compatible
- Prepare suction, irrigation, cautery, and microscope
- Perform full instrument and sharps count
Patient Positioning
- Position: Supine with head turned to the opposite side of surgery
- Head: Stabilised with a head ring or padded doughnut
- Support: Avoid pressure points with gel pads
- Arms: Tucked or extended based on anaesthetic preference
Skin Prepping and Draping
- Prep around the ear and posterior auricular area with betadine or chlorhexidine
- Apply fenestrated ENT drape, ensuring clear view for microscope access
- Confirm all equipment within sterile reach
3. Intraoperative Stages
- Incision: Postauricular or endaural based on surgeon preference
- Flap Elevation: Retract soft tissue to expose the mastoid cortex
- Drilling: Use cutting and diamond burrs to remove diseased air cells
- Exposure: Identify sinus plate, tegmen, and facial recess
- Disease Removal: Excise cholesteatoma or infected tissue
- Reconstruction: Graft placement if tympanoplasty or ossicular repair needed
- Haemostasis: Achieve with cautery, adrenaline-soaked patties, or gel foam
- Closure: Layered closure with sutures and pressure dressing applied
4. Post-Op Tasks
- Final instrument and sharps count
- Assist with drape removal and transfer to recovery
- Ensure documentation is complete and specimens sent if taken
- Clean, soak, and transfer instruments for sterilisation